Largest and fastest-growing economies in the world.
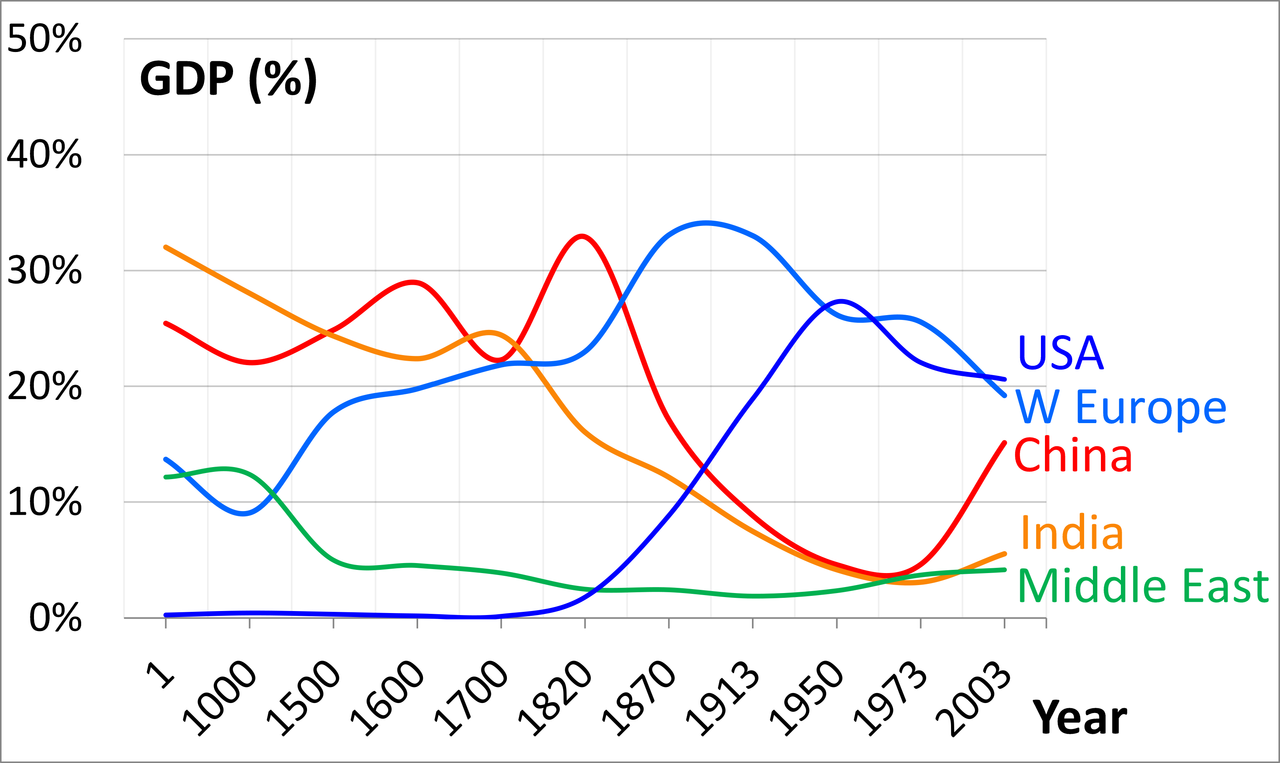
The Indian economy is one of the largest and fastest-growing economies in the world. Here are some key points about the Indian economy:
- GDP and Economic Growth GDP Size: India is the fifth-largest economy in the world by nominal GDP and the third-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP).
Growth Rate: India has a high growth rate compared to other major economies, although growth has been variable in recent years due to factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic and global economic conditions. - Demographics Population: India has a population of over 1.4 billion, making it the second most populous country in the world.
Demographic Dividend: A significant portion of the population is young, providing a potential demographic dividend if effectively harnessed through education and employment opportunities. - Key Sectors Agriculture: Contributes about 17-18% to GDP and employs a large portion of the population.
Industry: Includes manufacturing, mining, construction, and utilities, contributing around 27% to GDP.
Services: The largest sector, contributing about 55% to GDP, with IT and software services being particularly prominent. - Infrastructure and Development Urbanization: Rapid urbanization is driving infrastructure development in cities.
Government Initiatives: Programs like Smart Cities, Make in India, and Digital India are aimed at boosting infrastructure and industrial growth. - Trade and Foreign Investment Exports: Key exports include software services, textiles, jewelry, and pharmaceuticals.
Imports: Major imports include crude oil, gold, electronics, and machinery.
FDI: India has been a major recipient of foreign direct investment, especially in sectors like technology, telecommunications, and manufacturing. - Monetary and Fiscal Policy Reserve Bank of India (RBI): The central bank regulates monetary policy, including interest rates and inflation control.
Government Budget: Fiscal policy is driven by government budgets focusing on infrastructure, welfare programs, and economic reforms. - Economic Reforms GST Implementation: The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) simplified the indirect tax structure.
Banking Reforms: Initiatives to address non-performing assets (NPAs) and improve banking sector health.
Ease of Doing Business: Efforts to improve the business environment and attract investment. - Challenges Unemployment: High unemployment rates, particularly among youth, pose a significant challenge.
Poverty and Inequality: Despite economic growth, poverty and income inequality remain substantial issues.
Agricultural Distress: Farmers face challenges like low productivity, inadequate infrastructure, and market access. - Global Position Geopolitics: India plays a significant role in regional and global geopolitics, being a member of organizations like BRICS, G20, and the Commonwealth.
Trade Agreements: Actively engaged in forming bilateral and multilateral trade agreements to boost trade and investment. - Future Outlook Economic Projections: India is expected to continue its high growth trajectory, with potential to become one of the top three global economies in the next few decades.
Technological Advancements: Growth in technology sectors, particularly IT and digital services, is expected to drive future economic growth.
Sustainable Development: Increasing focus on sustainable and inclusive growth, addressing environmental challenges, and improving human development indices.